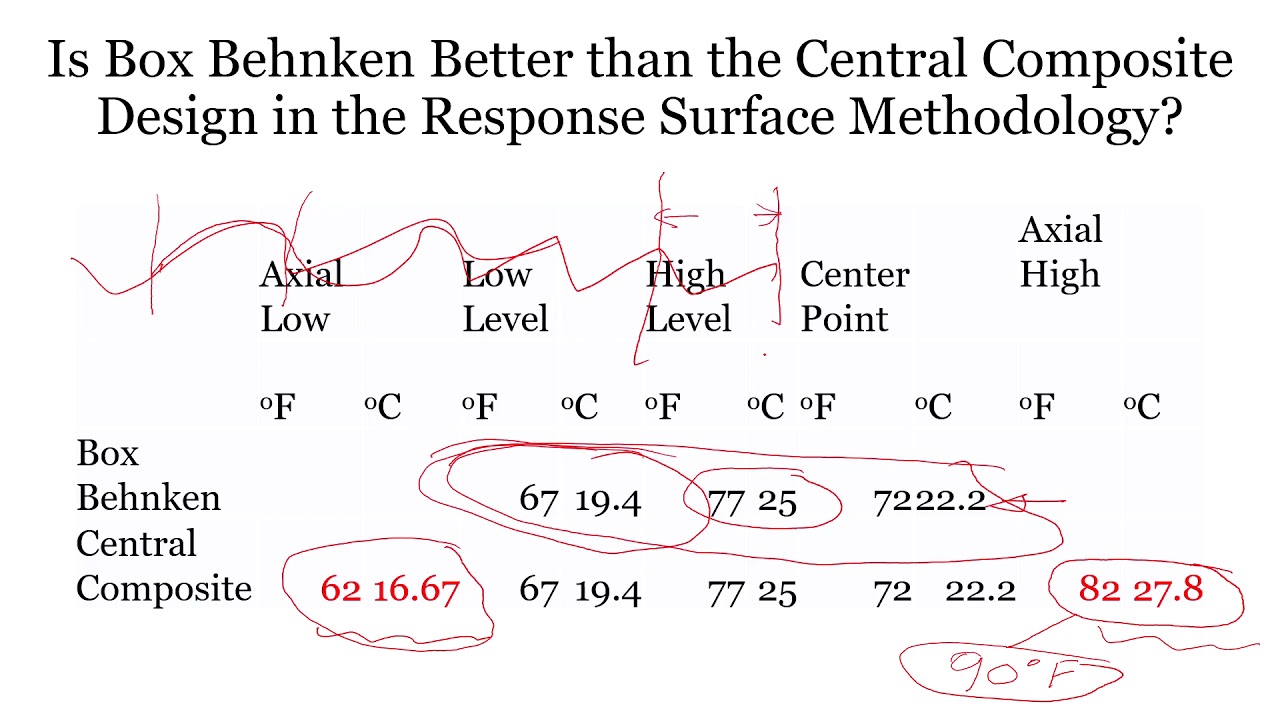
CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN VS BOX BEHNKEN
Variance is close for the two designs near the centre. However central composite design CCD D-optimal and Box-Behnken are found to be widely used optimization techniques for Fenton oxidation 1113 because of the advantage of optimizing multifactor problems with optimum number of experimental runs.
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Solving Order Planning Problem Using A Heuristic Approach The Case In A Building Material Distributor Html
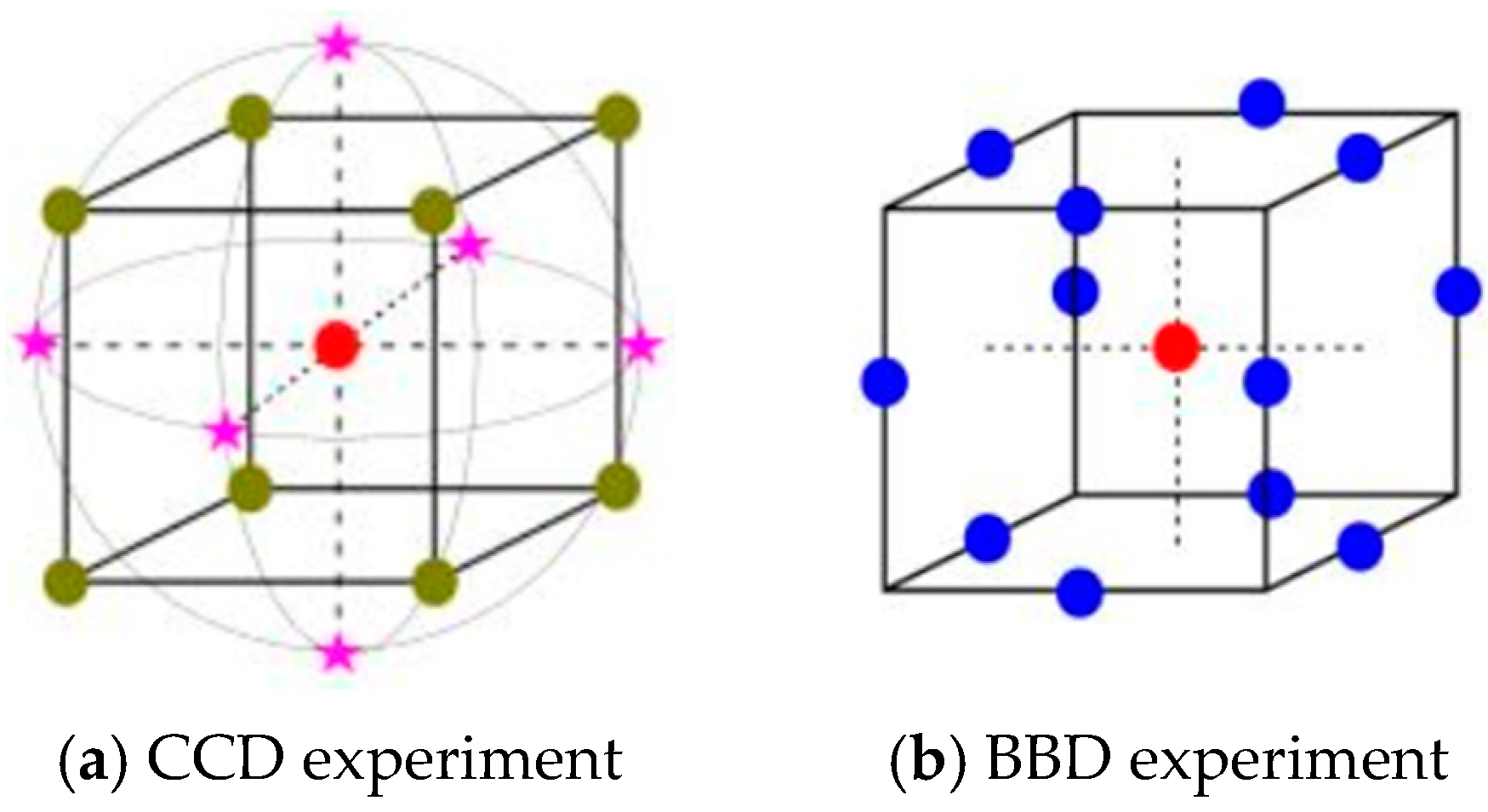
Compared to the Central Composite design it is missing the corner points it will never occur that all the factors are high or low at the same time No extreme combinations.

. Generally for more well-informed processes Box-Behnken could be more useful while the central composite could be more useful in relatively unknown processes. Two-level full factorial design central composite design Box-Behnken design and three-level full factorial design. The central composite plus Box-Behnken becomes a full factorial with three extra samples taken at the centre.
Variances of the central composite face-centered and BoxBehnken designs between radii 05 and 2 appear to be better for the central composite face-centered design. For 5 factors the Box-Behnken would have 46 observations and a central composite would have 52 observations if you used a complete factorial but this is where the central composite also allows you to use a fractional factorial as. Central composite designs usually have axial points outside the cube These points may not be in the region of interest or may be impossible to conduct because they are beyond safe operating limits.
Four experimental design types were applied. The RSM employs a three-level factorial design. Box-Behnken design is still considered to be more proficient and most powerful than other designs such as the three-level full factorial design central composite design CCD and Doehlert design despite its poor coverage of the corner of nonlinear design space.
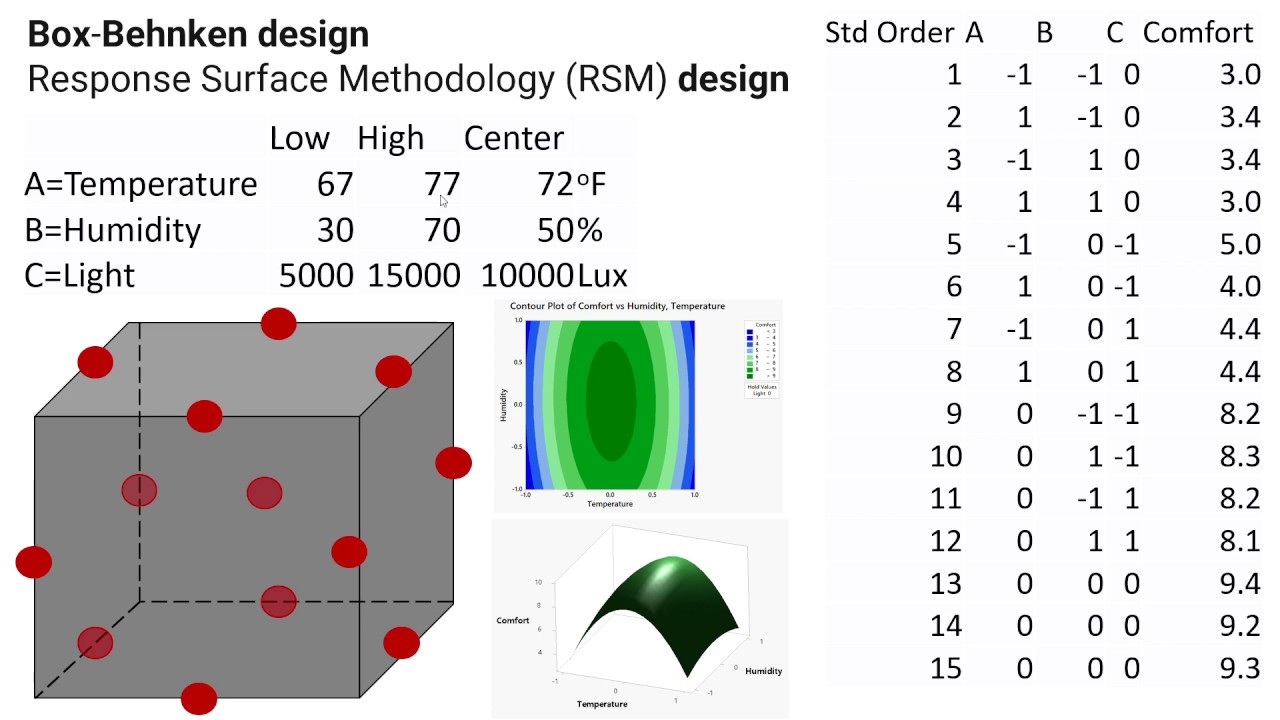
Besides these methods have limitation of increased number of experiments if several factors. With a Box-Behnken design every factor is having 3 levels compared to Central Composite 5 with 2 of. BB requires 3 different levels for each factor and 15 runs for 3 factors.
Central composite design and Box behnken design are used for prediction of machining parameters utilizing real experimental data set using MINITAB 17 software. Applied in combination with the full factorial design FFD 1-3 central composite design CCD 4-11 or Box-Behnken design BBD 12-14 serving for the data collection. Central Composite Design CCD Developed for estimating a quadratic model.
The BoxBehnken design shows a greater deviation from rotatability than the central composite face- centered design. For 5 factors the Box-Behnken would have 46 observations and a central composite would have 52 observations if you used a complete factorial but this is where the central composite also allows you to use a fractional factorial as. Box-Behnken design is having the maximum efficiency for an experiment involving three factors and three levels.
The Box-Behnken design uses the twelve middle edge nodes and three centre nodes to fit a 2nd order equation. Up to 10 cash back The BoxBehnken design shows a greater deviation from rotatability than the central composite face-centered design. They are comprised of a standard 2k factorial center points and axial points.
Box-Behnken designs place points on the midpoints of the edges of the cubical design region as well as points at the centre. Variance is close for the two designs near the centre. Comparing the central composite design with 4 factors which has 31 observations a Box-Behnken design only includes 27 observations.
Designs that are more practical than the three-level factorial designs are Central Composite and Box Behnken designs. The proposed Box-Behnken design requires 15 runs of experiment for data acquisition and modeling the response surface. Box-Behnken design BBD central composite design CCD and D-optimal design Rakić et al 2014.
Further the number of experiments conducted for this is much lesser compared to a central composite design. Created from a two-level factorial design and augmented with center points and axial. 29 rows As you can see there are less data point needed compared with a Central Composite design.
The Box-Behnken design is an independent quadratic design in that it does not contain an embedded factorial or fractional factorial design. The Central Composite design is based on a two-level factorial design with the addition of 2 k k is the number of independent variables points star points between the axes plus repeat points at the centroid. Development of better predictive model compared to other techniques.
To help you choose the best design for your experiment Ive put together a list of things you should know about each of the three primary response surface designsCentral Composite Box-Behnken and Optimal. Box-Behnken These designs require fewer treatment combinations than a central composite design in cases involving 3 or 4 factors. The Plackett-Burman design followed by either CCD 15 or Box-Behnken design 16-18 has also been applied in optimizing liquid-solid extraction processes.
BBD is considered. This means it is significantly easier for DoE rather than for BB as less time will be required and no runs will include factors outside the minmax values of the studied area. Central composite designs are much more flexible with respect to the issue of 2 way interactions.
These designs are rotatable or near rotatable and require 3 levels of each factor. Vera Candioti et al 2014. In this design the treatment combinations are at the midpoints of edges of the process space and at the center.
Because their core is a 2k factorial you have the option of running a full factorial at the center or if you don t desire information on some or all of the 2 way interactions you can run the core as. They can be less expensive to do than central composite designs with the same number of factors. The Box-Behnken design is rotatable or nearly so but it contains regions of poor prediction quality like the CCI.
Variances of the central composite face-centered and BoxBehnken designs between radii 05 and 2 appear to be better for the central composite face-centered design. This could be the reason why the central composite design is used more than the Box-Behnken design because most studies are conducted on to find something new. Box-Behnken design often has fewer design points.
CCD on the other hand requires 5 different levels and 20 runs for 6 central points. Box-Behnken designs do not have axial points thus you can be sure that all design points fall within your safe operating zone. The advantages and drawbacks of each design are described and detailed statistical evaluation of.
Comparing the central composite design with 4 factors which has 31 observations a Box-Behnken design only includes 27 observations.
Design Of Experiments Statistics Toolbox

Central Composite Design An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Central Composite Design An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Experimental Design For Three Design Variables A Full Factorial Download Scientific Diagram
Box Behnken Response Surface Methodology Rsm Design And Analysis Example Using Minitab Ms Excel Youtube
Is Box Behnken Better Than The Central Composite Design In The Response Surface Methodology Youtube
Experimental Designs In Three Variables For Fitting Second Order Models Download Scientific Diagram

%20Number.png)
Belum ada Komentar untuk "CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN VS BOX BEHNKEN"
Posting Komentar